The sales/collection process (also referred to as the sales process or the revenue process) includes activities related to the sale of goods or services. These activities include everything from sales calls and other marketing activities to collecting cash from customers. Whether firms are manufacturers, merchandisers, or service businesses, their sales processes, are similar. Manufacturing and merchandising firms sell products to customers; service firms perform services for customers. Generally, customers place orders for products or services they are purchasing. Then, the selling firm ships the products or performs, the services. Customer, pursuant to the terms of the sale, pay the amount due in one or more payments before, during, and/or after the sale.
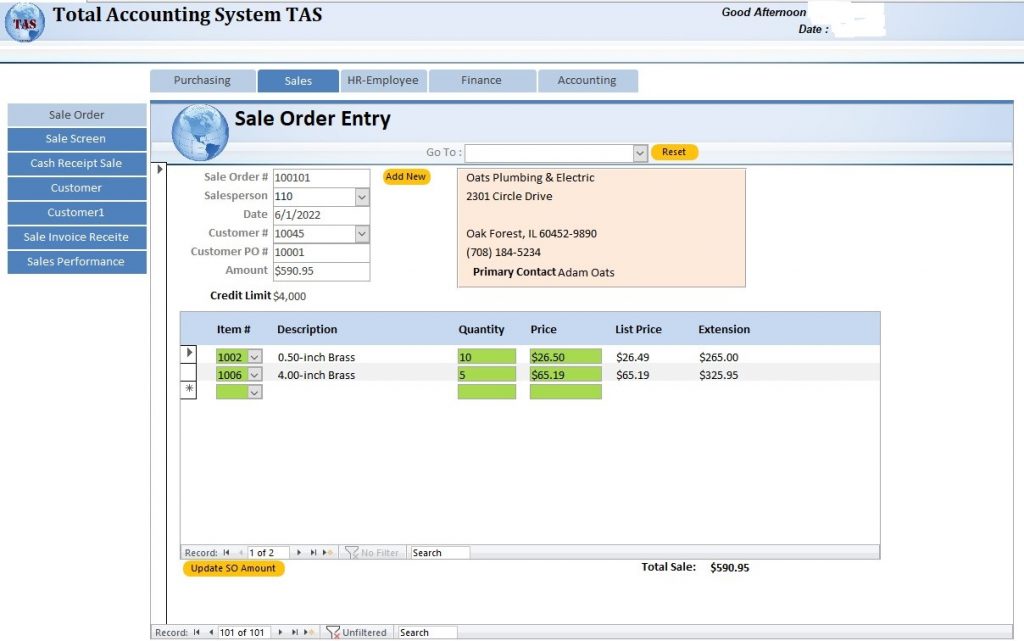
Business Process Firms accept orders over the telephone and via fax, e-mail, and regular mail. When an order arrives, one of the salespersons enters it into the system as a sale order. The sale order includes the customer’s name and a list of inventory items the customer wishes to purchase. This inventory list includes the quantity of each inventory item ordered and its actual sale price. The actual sale price may differ from the item list price stored for that item in the inventory table if the item is on sale or the firm decide to offer a discount for a particularly large quantity ordered. The firm sends a confirmed sale order back to the customer for the customer’s records. When the order is ready to ship, a materials handler uses the sale order information to pick the ordered merchandise from the warehouse, pack it in boxes, and load it on a delivery truck. When the goods are loaded on the truck, the firm record the sale and print an invoice as the firm always ships goods FOB shipping point. FOB shipping point means that title changes hands when the goods leave the seller’s premises, and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GSAP) state that a sale is generally recorded when title changes hands. Sometimes, some items a customer has ordered are not in stock. When this occurs the firm ships a partial order. Customers are expected to pay their invoices within 30 days. Most customers pay on time with only one payment. However, some customers arrange to make partial payments over two or more months. TAS will assume that each customer payment relates to only one invoice. Payments received are always deposited into only one bank account, usually the operating account.